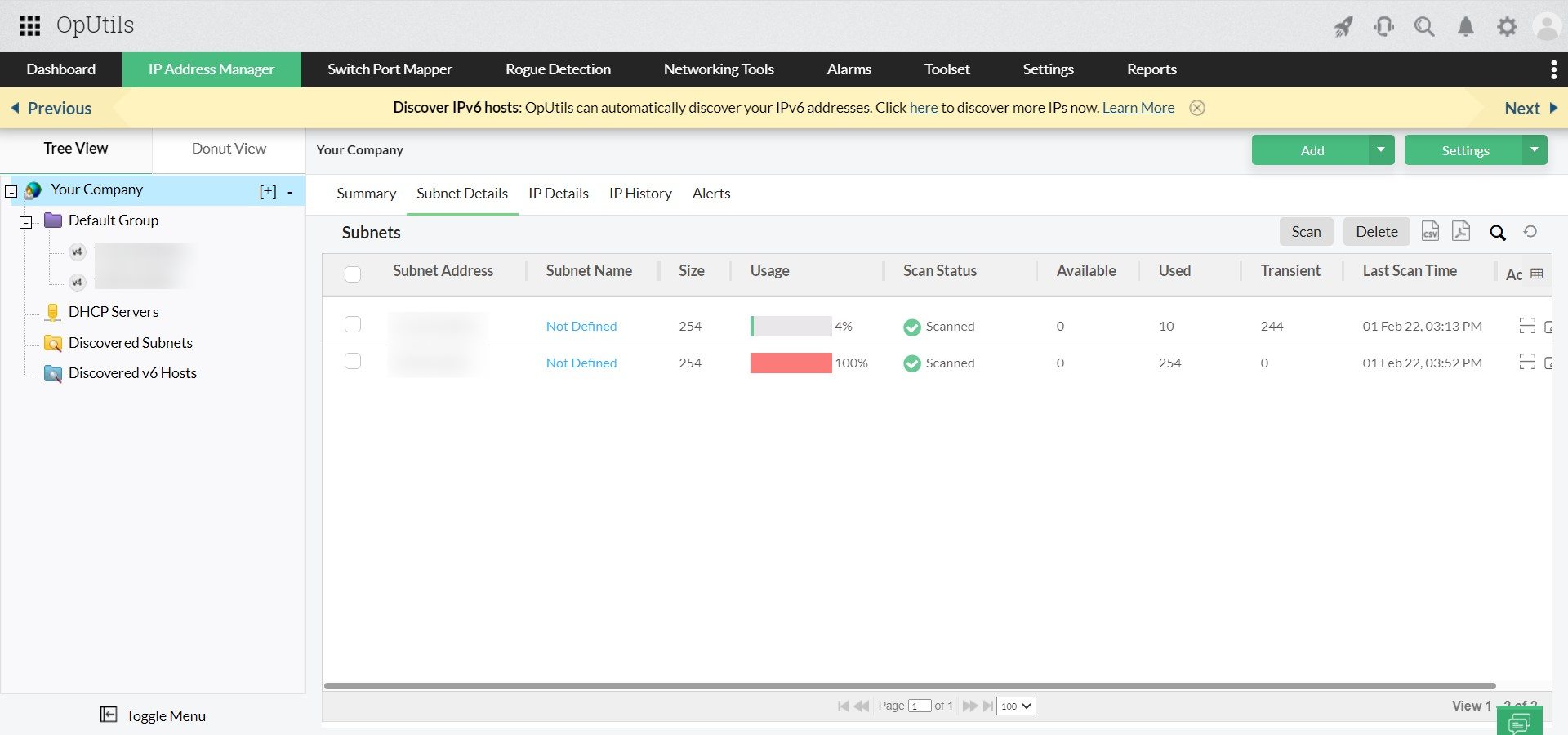
Ip Address Management For Mac
ManageEngine launches OpUtils which is a web-based IP address Management tool. It provides a centralized managemen t of the IP address space, including IPV4 and IPv6 Address Management. This tool tracks and monitors various IP address related information that a network engineer needs to administer and effectively manage a network’s address space.
Z945c010 motherboard driver for mac. Zc sound driver for mac This Software is licensed for z945c010 sound only in conjunction with Intel component products. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or z945c010 sound the Software. Try to set mercury gvm motherboard system restore point before installing a mercury motherboard 845gvm driver. Return form will be sent to mercury motherboard 845gvm email Id: He is a lifelong computer geek and loves everything related to computers, software, pilm-l new technology. ZC MOTHERBOARD DRIVERS FOR MAC DOWNLOAD. Z945c010 motherboard your manufacturer, product line, and specific model number and it should tell you what kind of memory is compatible with your machine. Try a different LAN cable. Welcome to Z945c010 motherboard 7 Forums. Find More Posts by Zc motherboard. ASUS M2V-MX MOTHERBOARD DRIVERS FOR MAC DOWNLOAD - Check local regulations for disposal of electronic products. ASUS MyLogo You can convert your favorite photo into a color boot logo for a more colorful.
What is the difference between a MAC Address and an IP Address? Are both traceable back to your computer? And can you hide them? If by hiding them is your computer safer from hackers. Also, are the free versions as good as the ones you buy? Well, the last one is easy to answer: there’s no concept of free versus paid IP or MAC addresses. As you’ll see in a moment, IP addresses are assigned as part of connecting to a network, and MAC addresses are assigned at the time hardware is manufactured.
Even hiding a MAC or IP address is a concept that doesn’t quite apply, but we’ll get in to that too. And whether MAC or IP addresses are hidden or not, they are not the kind of things you should be spending your time worrying about to stay safe from hackers. Become a and go ad-free! MAC Address A MAC (or Machine Access Control) address is best thought of as kind of serial number assigned to every.
No two anywhere should have the same MAC address. (I’ll talk about that “should” more in a moment.) You can see your network adapter’s MAC addresses by using the command prompt in Windows with the ipconfig /all command.
It looks something like this: Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection 2:. Physical Address.: 00-1D-60-2F-4B-39 Each network adapter on your computer, including wired and wireless interfaces, has one. MAC addresses are typically used only to direct packets from one device to the next as data travels on a network. That means that your computer’s network adapter’s MAC address travels the network only until the next device along the way. If you have a router, then your machine’s MAC address will go no further than that.
The MAC address of your router’s internet connection will show up in packets sent further upstream, until that too is replaced by the MAC address of the next device – likely either your modem or your ISP’s router. Bottom line: your MAC address doesn’t make it out very far. Even if someone knows your MAC address, that knowledge certainly doesn’t help them do anything either good or bad. IP address An is assigned to every device on a network, so that device can be located on that network. The internet is just a network, after all – albeit a huge one – and every device connected to it has an IP address. The server that houses Ask Leo!, for example, is (currently) at 50.28.23.175. That number is used by the network routing equipment, so when you ask for a page from the site, the request is routed to the right server.
The computers or equipment you have connected to the internet are also assigned IP addresses. If you’re directly connected, your computer will have an IP address that can be reached from anywhere on the internet. If you’re behind a router, that router will have the internet-visible IP address, but it will then set up a separate, private network to which your computer is connected, assigning IP addresses out of a private range that is not directly visible on the internet. Any internet traffic your computer generates must go through the router, and will appear on the internet to have come from that router.
The mailroom metaphor Metaphors are always a tad difficult, but let’s try this. An IP address is kind of like your postal address. Anyone who knows your postal address can send you a letter. That letter may travel a simple or complex route to get to you, but you don’t care, as long as it makes it.

The same is true of packets of data traveling on a network like the internet. The IP address indicates the computer to which a packet is destined, and the system takes care of getting it there.
A letter may or may not also have a return address so you know who to write back to, but a TCP/IP address always has a return IP address. A router can perhaps be thought of as a company’s mail clerk. You may send a letter to “Complaint Department, Some Big Company, Some Big Company’s Address”. The postal service will get that letter to the company.
The company’s mail clerk then notes that the letter needs to go to the complaint department, and routes it there using inter-office mail. And of course, all your outgoing mail is picked up by the clerk and routed to the external postal service as needed. When you’re behind a router, the same thing sort of happens. All of the packets destined for you are actually addressed to your router.
The router then determines which of your computers that packet is meant for, and routes the packet appropriately (hence the name router). Whether corporate mail room or networking router, neither the actual physical location of your office within your company’s building, or the actual local IP address of your computer on your local, private network is visible to the outside world.
A MAC Address is kind of like the color, size, and shape of your physical mailbox. It’s enough that the mail clerk (your network router) can identify it, but it’s unique to you. There’s no reason that anyone other than your postal carrier might care what it is, and you can change it by getting a new mailbox (network card) at any time and slapping your name (IP address) on it, without affecting your delivery. As I said, it’s not a perfect metaphor, but perhaps it’ll help get some of the basic concepts across. MAC addresses and staying safe.
When it comes to staying safe, MAC addresses aren’t part of the discussion, because they never travel beyond your local network, and they can’t be hidden, as they’re required for networking to work. Many network adapters allow you to override the MAC address, but even so, it still identifies your computer on the local network.
IP addresses are also required for networking to work. The network has to know which computer to send data to. You can, in many cases, use things like anonymization services and the like to appear to be coming from a different IP address, but that doesn’t change the fact that your machine is still reachable by some IP address. And, to be clear, it is quite possible for your MAC address, or your local IP address, to be read by software – that’s how the IPCONFIG command we saw earlier was able to show it to you. Other software could do the same, and even send that information on to someone else for some reason. But it does them no good. Knowing your MAC address, or your local IP address, doesn’t help me if I’m not on the same local network as your machine.
Being connected to the internet, by whatever means, requires that you. There’s ultimately no way to completely “hide” your IP address without disconnecting from the network. What you should be doing are the classical steps to internet safety: get behind a router, keep your system up to date, run anti-malware scans, backup regularly, and so on. A word about tracing A MAC address cannot be traced, as it is only associated with a machine, not a location. If somehow captured, which would require additional software on the machine, it could strongly identify a specific computer. Since MAC addresses can be changed in software on many network adapters, it’s not necessarily possible for a MAC address to positively identify a machine.
Since I know it’ll come up, and as I’ve discussed and and and again, an IP address does not allow someone to find out your physical location or identity without law enforcement intervention. Similarly, you cannot find out someone else’s physical location or identity without involving the authorities. In this scenario, you'll end up with two IP addresses, but the hub and router won't each get one. I'll explain.
A MAC address can easily be traced for as far as it travels. The problem is, a MAC address doesn't travel far enough to be useful. When your computer can't get an IP address any other way, it assigns itself a 169.254 IP address.
It's a sure sign of a problem. Comparing your machine's IP address to that reported by a website may result in a surprising difference. I'll explain why that is and why it's a good thing. Posted: January 21, 2016 in: Shortlink: TAGS:,. It’s funny you use a postal metaphor here.
My father once asked me how his computer “knows” how to talk to a computer across the country. I used a postal metaphor to describe how Internet traffic is routed.
When you mail a letter, how does the letter “know” how to get across the country? It doesn’t have to. The postman who picks up the mail only has to know how to get it from your mailbox to the local post office.
My Ip And Mac Address
Someone at the local post office only has to know that a letter going to Florida gets sent to the White Plains post office. From there, someone only has to know that it goes to the New York City branch. From there, someone sends it on a truck to Miami. From there, it’s put on a truck to the local post office.
And from there, it’s put on a truck to be delivered. At each step, all that’s needed to be known is which direction to send it on its next step along the way.
Leo – one part of the original question asks about the difference between IP addresses you get ‘for free’ and those you buy. I think this is asking about the difference between a dynamic and a static IP address – most ISPs will give you a dynamic IP address as standard but will charge you for a fixed IP address; a dynamic IP address is fine if you just use email and the internet, but if, for example, you want to run your own web server, and host it yourself on your own computer, you need a static IP address. MAC addresses are actually at a lower ‘level’ than IP in the 7-layer OSI model of networking. (No you don’t have to understand it to use it. ) Your local area network (LAN) almost always uses “Ethernet” as the under-lying network technology; Ethernet uses MAC addresses to figure out where packets go, not IP addresses. Ethernet usually stops at your ISP router which is why the MAC addresses also stop there.
Think: Internet uses TCP/IP (Network layer 3 & 4) whereas Ethernet uses MAC (Network layer 1 & 2) to send information. See the Wikipedia article on the OSI model for more. Chandra, Say, for instance, you are a network admin, and somewhere in your network, there is an infected device on port 1. So you go to the office only to find that there is no longer any device plugged in to port 1. If you only used the port 1 information, you would not be able to positively identify the infected device because the device is no longer plugged into port 1. The only way to truly identify that the infected device is using the MAC address. The purpose of a MAC address (among other things) is to positively and uniquely identify a device.
Dear Leo, this information is really very valuable. I have a keen interest in network security methods in current times and I wanted to ask something to clarify some things for myself I have a system that connects to a router which further connects to my modem. When i do ipconfig/all, i get the mac address of my ethernet port, not the router or modem, which i can check using the interface for the respective device. If my understanding is correct, my mac address does not go past the router, coz it changes there to the address of the router which further changes to the address of the modem and so on however, at the site “it uses java to find the mac address of my ethernet card. This is what brings me to my question as you said, “So your MAC address doesn’t make it out very far.
Even if someone knows your MAC address, that knowledge certainly doesn’t help anyone do anything either good or bad.” just as the site used java to find my original mac address, can’t a similar process be applied to trace a person/machine’s location on the internet. Also, there are proxy service providers, both free and paid softwares, that change the external ip address of a machine. In theory, is ip address tracking the only professional way of tracing a person/machine’s original address? My understanding is that the sender’s ip is included in the chat/email/post that is received at the other end, and these proxy servers/softwares change that header info to keep it anonymous.
I know legal intervention is required, but is the packet info that contains the IP address the only way of tracing the origin or does it also have mac address info of the originating machine/person? Please help me understand this better. Thanks in advance. Best Regards. Hi.Leo i wanna know that how the webcam chat rooms sites banned us?what those sites use to identityfy us?
I usually use vagaters.com for webcam chat with friend all over country. Some day ago i did the text flooding so vagaters.com blocked me and say pls return after 3 hrs. I came back to the vagaters.com and tried to login but it return me access denied! Now i m not able to login vagaters.com.i m trying to login each time but i cant always i found Acess Denied! So what can i do should i need to change my IP address or MAC address? Hi.Leo i wanna know that how the webcam chat rooms sites banned us?what those sites use to identityfy us?
I usually use vagaters.com for webcam chat with friend all over country. Some day ago i did the text flooding so vagaters.com blocked me and say pls return after 3 hrs.
I came back to the vagaters.com and tried to login but it return me access denied! Now i m not able to login vagaters.com.i m trying to login each time but i cant always i found Acess Denied! So what can i do should i need to change my IP address or MAC address? Note-vagaters.com do not require any login info and email address for login.Every one can login as guest using any of user name and u can also login using another username,no passward require.
I like your metaphor/analogy. I’ve tried to explain that concept not so much from a “How to be safe from hackers” perspective, but to answer the question “Why didn’t I get my e-mail?” or “Why did it take so long to send/receive my e-mail?” I like your explanation better than mine.
They’re similar, but your description makes more sense! I usually start by trying to clarify that an address is an address – Internet or home address – & that it’s a unique, identifiable thing.
Something that can be found on a map or schematic. Half the time I lose them after using the word schematic, but either way – lose them there or not – I can NEVER find the words to make it understandable! I’ll continue my explanation by saying, “It’s like having mail carrier pick up a letter from a sender’s address with the end result being that it will be delivered to the receiver’s address. The recipient will usually receive the it in the time frame expected but – depending on all the magic (good & bad) behind the scenes – it might arrive late or never at all. Then I try to define magic thustly: If the mail truck crashes for some unexplainable reason & every piece of mail becomes ash, you’ll never get your delivery & probably never know why; if the mail person gets sick there might be a delay while the post office finds a subsitute carrier; maybe there’s roadwork on your street & the mail person has to take a detour that results in a longer drive or walk so it takes longer than it should. Then I’ll add that sometimes a package is so big & heavy it has to be broken down into individual pieces & delivered separately – but there’s a magician type of thing that reassembles the smaller packets into the bigger package before you actually receive it. Of course by then they’re saying, “Uh nevermind” or “I’m not asking about SNAIL mail.” Oh boy.
Sometimes when someone asks why they didn’t recieve an e-mail I tell them they’d have better luck getting an explanation if they direct their question to the Goddess of Null. I THINK they know I’m trying to be funny!
I’m always being asked if I’m a computer tech because I’m crazy or if being a computer tech MADE me crazy. I tell them I don’t know for sure because I’m crazy! Never a dull moment that’s for sure! I hope it’s OK if I use YOUR explanation of data transfer in the future. Recently one incident happened in our office.
Someone sent emails from rediff to one girl and the IP address shown was of our office.The police found our office IP and they found some port no. 7 which was connected to one of my friends PC. I am confused how the ISP gave port no.7 as culprit. My friend is genuine and he hasnt done aytign wrong. Can you tell me: 1) How ISP would have found the port no. 2) when email accounts are created on rediff, do they not have mac id saved of users pc? 3) Does router also have a Mac id?
4) they got some mac id which isnt matching any pc in office, but no one changed aything in any pc, what would have happened. Assuming the simple case typical for most users, with one ‘Internet connected’ Router and multiple devices IPADs, Desktop PCs, Notebook PCs connected and accessing the Internet: MAC addresses are allocated to network devices.
Most devices will have a single MAC address but laptops typically have two, one for the NIC and one for the wireless. MAC addresses were originally meant to be pre-allocated and unchangeable but some devices often home Internet routers allow MAC addresses to be changed. They must be unique on a network; you WILL have problems on networks if you connect devices with duplicate MAC addresses. They are only seen on the network to which you’re connected; Email/http etc. Requests from a device will have the Router’s MAC address on the Internet Packet when it leaves the building. IP addresses are also allocated to network devices that are enabled and connected. If you connect a laptop wirelessly and with an Ethernet cable to your Router, you will have two IP addresses, one for the network cable with the cable pugged in and one for the wireless adapter.
As above; email / http etc. Requests from a device will have the Router’s IP address on the Internet packet when it leaves the building. Before commenting please:. Read the article. Comments indicating you've not read the article will be removed. Comment on the article.
New question? Start with search, at the top of the page. Off-topic comments will be removed. No personal information. Email addresses, phone numbers and such will be removed. Add to the discussion.
Comments that do not — typically off-topic or content-free comments — will be removed. All comments containing links will be moderated before publication. Anything that looks the least bit like spam will be removed. I want comments to be valuable for everyone, including those who come later and take the time to read.
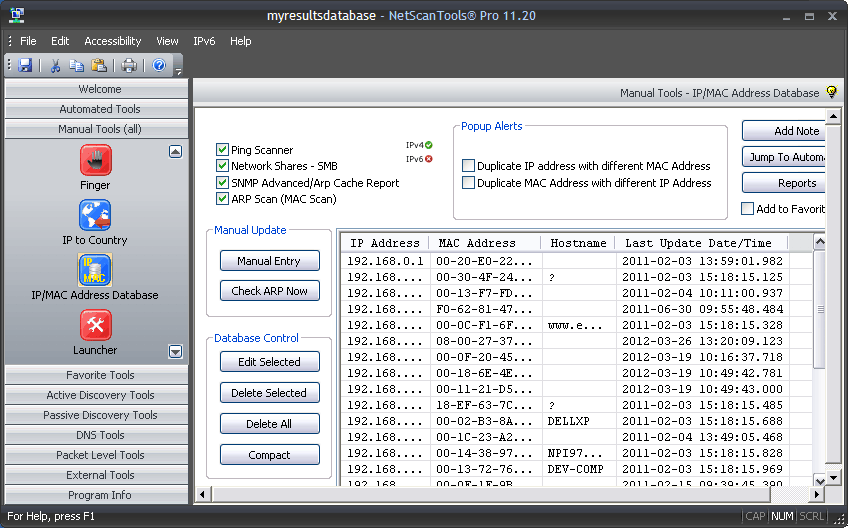
NetScanTools Pro IP/MAC Address Management Tool Description The IP/MAC Address Management tool is a database tool designed to maintain IPv4/MAC address associations found using the and the. IP/MAC address associations are gathered from the Ping Scanner following a ping sweep. IP/MAC address associations are gathered from the Network Shares - SMB. IP/MAC address associations are gathered from the SNMP ARP Cache Report.
Find My Mac Ip Address
IP/MAC address associations are gathered from ARP Scan. IP/MAC address associations can be manually entered or updated using the Check ARP Now button. Popop window alerts can be optionally issued if an IPv4 address is found with a different MAC address or vice versa. IP/MAC address associations are time stamped in the database and the hostname is also retained if it is known. The database is SQLite.